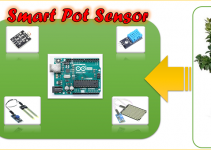
Nell’articolo “Un sistema Multisensoriale per la Smart Home – Parte 1” abbiamo descritto i componenti del progetto Multisensore, il funzionamento del circuito e come realizzarlo utilizzando lo schema elettrico riportato nella Figura 4 dell’articolo Parte 1. Abbiamo installato nella scheda D1 Mini il driver del chip CH340 e alcune librerie di gestione dei sensori, infine, abbiamo testato il funzionamento del modulo D1 Mini mediante il programma di esempio Blink.
Verificata con successo l’esecuzione del programma Blink, abbiamo la certezza che la scheda D1 Mini funziona correttamente, quindi possiamo procedere con la programmazione del modulo D1 Mini caricando il codice ESP8266_Multisensor_Shield.ino. Dall’editor di Arduino, aprite un nuovo sketch e copiate il codice seguente:
/***************** ESP8266_Multisensor_Shield.ino ********/
/***************** ESP8266_Multisensor_Shield.ino ********/
// Load libraries
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <EEPROM.h>
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "IL TUO SSID";
const char* password = "LA TUA PASSWORD";
// Auxiliary variables for temperature
static char celsiusTemp[7];
static char fahrenheitTemp[7];
String temperatureString = "";
// Variable to hold the temperature reading
// EEPROM size
// Address 0: Last output state (0 = off or 1 = on)
// Address 1: Selected mode (0 = Manual, 1 = Auto PIR,
// 2 = Auto LDR, or 3 = Auto PIR and LDR)
// Address 2: Timer (time 0 to 255 seconds)
// Address 3: LDR threshold value (luminosity in percentage 0 to 100%)
#define EEPROM_SIZE 4
// Set GPIOs for: output variable, status LED, PIR Motion Sensor, and LDR
const int output = 15;
const int statusLed = 12;
const int motionSensor = 5;
const int ldr = A0;
// Store the current output state
String outputState = "off";
// GPIO where the DS18B20 is connected to
const int oneWireBus = 4;
// Setup a oneWire instance to communicate with any OneWire devices
OneWire oneWire(oneWireBus);
// Pass our oneWire reference to Dallas Temperature sensor
DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire);
// Timers - Auxiliary variables
unsigned long now = millis();
unsigned long lastMeasure = 0;
boolean startTimer = false;
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
unsigned long previousTime = 0;
const long timeoutTime = 2000;
// Auxiliary variables to store selected mode and settings
int selectedMode = 0;
int timer = 0;
int ldrThreshold = 0;
int armMotion = 0;
int armLdr = 0;
String modes[4] = { "Manual", "Auto PIR", "Auto LDR", "Auto PIR and LDR" };
// Decode HTTP GET value
String valueString = "0";
int pos1 = 0;
int pos2 = 0;
// Variable to store the HTTP request
String header;
// Set web server port number to 80
WiFiServer server(80);
void setup() {
// Start the DS18B20 sensor
sensors.begin();
// Serial port for debugging purposes
Serial.begin(115200);
// PIR Motion Sensor mode,
then set interrupt function and RISING mode
pinMode(motionSensor, INPUT_PULLUP);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(motionSensor),
detectsMovement, RISING);
Serial.println("start...");
EEPROM.begin(EEPROM_SIZE);
// Uncomment the next lines to test the values stored in the flash memory
/*Serial.println(" bytes read from Flash . Values are:");
for(int i = 0; i < EEPROM_SIZE; i++) {
Serial.print(byte(EEPROM.read(i)));
Serial.print(" ");
}*/
// Initialize the output variable and the LED as OUTPUTs
pinMode(output, OUTPUT);
pinMode(statusLed, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(output, HIGH);
digitalWrite(statusLed, LOW);
// Read from flash memory on start
and store the values in auxiliary variables
// Set output to last state (saved in the flash memory)
if(!EEPROM.read(0)) {
outputState = "off";
digitalWrite(output, HIGH);
}
else {
outputState = "on";
digitalWrite(output, LOW);
}
selectedMode = EEPROM.read(1);
timer = EEPROM.read(2);
ldrThreshold = EEPROM.read(3);
configureMode();
// Connect to Wi-Fi network with SSID and password
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
// Print local IP address and start web server
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected.");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
}
void loop() {
WiFiClient client = server.available();
// Listen for incoming clients
if (client) {
// If a new client connects,
currentTime = millis();
previousTime = currentTime;
Serial.println("New Client.");
// print a message out in the serial port
String currentLine = "";
// make a String to hold incoming data from the client
while (client.connected() && currentTime-previousTime <= timeoutTime)
{
[...]
ATTENZIONE: quello che hai appena letto è solo un estratto, l'Articolo Tecnico completo è composto da ben 2697 parole ed è riservato agli ABBONATI. Con l'Abbonamento avrai anche accesso a tutti gli altri Articoli Tecnici che potrai leggere in formato PDF per un anno. ABBONATI ORA, è semplice e sicuro.